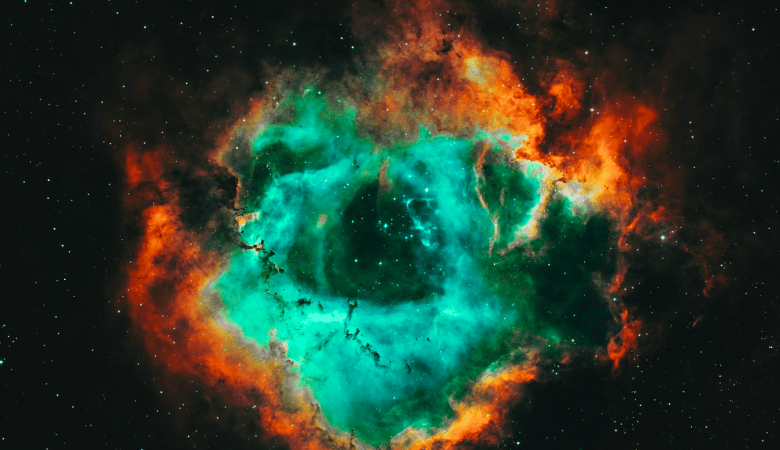
The Rosette Nebula stands out as a breathtaking spectacle in the vast expanse of our universe, filled with countless wonders and celestial bodies, capturing the imaginations of astronomers and stargazers alike. Located approximately 5,200 light-years away from Earth, this astronomical marvel resembles a gigantic rose floating in space, making it a stunning feature of our Milky Way Galaxy. This nebula is intricately linked to a cluster of stars known as NGC 2244, which resides within the nebula’s core, illuminating and shaping its surroundings.
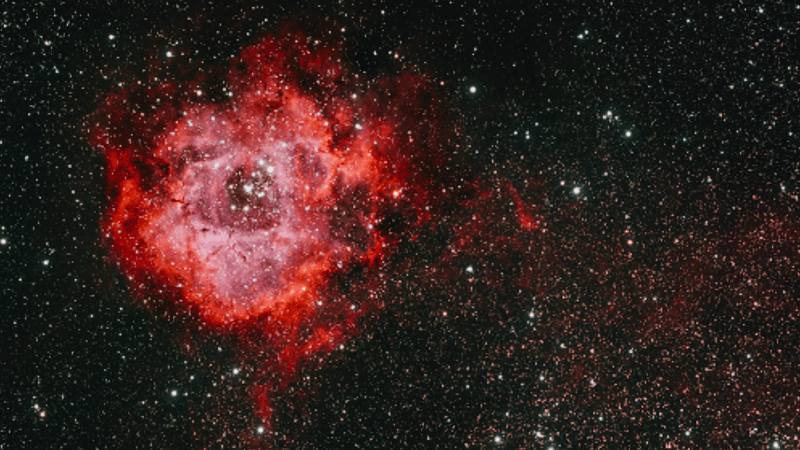
The Rosette Nebula, positioned at one edge of the Milky Way, is a stellar nursery where new stars are born from the nebula’s gaseous and dusty material, known as “nebulosity.” The stars embedded within this nebula emit intense energy, which in turn causes the surrounding gas to glow brilliantly. The nebula’s distinct red hue is a result of this interaction, where the light from these stars strips electrons from the hydrogen atoms within the cloud, leading to a glowing emission in the red part of the spectrum.
Deep within the Rosette Nebula, a dynamic process of star formation unfolds. Protostars, or infant stars that are still in the process of forming, dot the landscape, alongside jets of gas and dust that shoot out into space. Dense regions known as “Bok globules” harbor the seeds of future stars, waiting for their chance to shine. These areas of concentrated matter are the birthing grounds of new celestial bodies, adding to the complexity and beauty of the nebula.
Moreover, the Rosette Nebula is sculpted by the forces of stellar winds and intense radiation emanating from the sun and nearby stars. These forces carve out dark, trunk-like structures within the cloud, creating a tapestry of light and shadow. The intricate patterns and shapes seen within the nebula are the result of these energetic interactions, showcasing nature’s ability to craft awe-inspiring formations in the cosmic realm.
The unique rose-like appearance of the nebula is attributed to the combined effects of stellar winds, radiation pressure, and other invisible forces at play in space. This natural cosmic phenomenon demonstrates the universe’s capacity for creating mesmerizing patterns and structures that captivate our curiosity and desire to explore the unknown.
Also referred to as Caldwell 49, the Rosette Nebula resides in a region of our galaxy known as Monoceros, named after the constellation in which it is found. Its striking resemblance to a rose, and at times to a human skull, has earned it the nickname “Skull Nebula” among some observers. This duality in appearance only adds to the intrigue and fascination surrounding this celestial body, making it a favorite subject of study and admiration among astronomers and enthusiasts around the world.
The Rosette Nebula’s blend of natural beauty, scientific interest, and the mysteries still to be unraveled make it a compelling destination in the cosmic journey of discovery. As we continue to explore the universe, phenomena like the Rosette Nebula remind us of the incredible diversity and splendor that exists beyond our home planet, inspiring us to keep looking up and wondering about the vastness of space that surrounds us.